The rising adoption of connected car technology in the auto industry has resulted in various benefits. Increased efficiency, aftersales revenue, and a customized driving and vehicle ownership experience are some of the major benefits. However, as connected vehicles become more prevalent, there is a growing need for stronger cybersecurity and data privacy since these vehicles store and transfer massive volumes of sensitive data. Do you really know how your data is handled? Find out the different aspects of cybersecurity from this article.

Cybersecurity threats of data collection from vehicles
Threats to connected vehicles’ cybersecurity could originate from a range of sources, including hacking, malware, and phishing attacks. These risks could lead to unauthorized access to sensitive data, like information about the driver and passengers, and the vehicle’s operating systems. In the worst-case scenario, these assaults may result in the attacker gaining physical control of the vehicle.
Maximum cybersecurity protocols
To keep drivers and passengers safe and to protect their privacy, telematics companies must put cybersecurity and data privacy at the top of their list of priorities. This entails implementing strong security measures, such as encryption and multi-factor authentication, to prevent unauthorized access to important data.
Also, these companies must make sure they follow rules about data protection, like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
This involves not only protecting the data generated by connected vehicles but also ensuring that we collect and utilize it in a transparent and ethical manner.
Making sure that over-the-air (OTA) software updates are secure is another important part of cybersecurity and data privacy for connected vehicles. Because addressing vulnerabilities and enhancing vehicle functioning is critical, it is essential to perform these upgrades in a safe and dependable manner. To achieve this, we must use secure and reliable communication protocols and protect the vehicle’s systems from unauthorized access during the update process.
Connected Cars operating with the highest level of data privacy
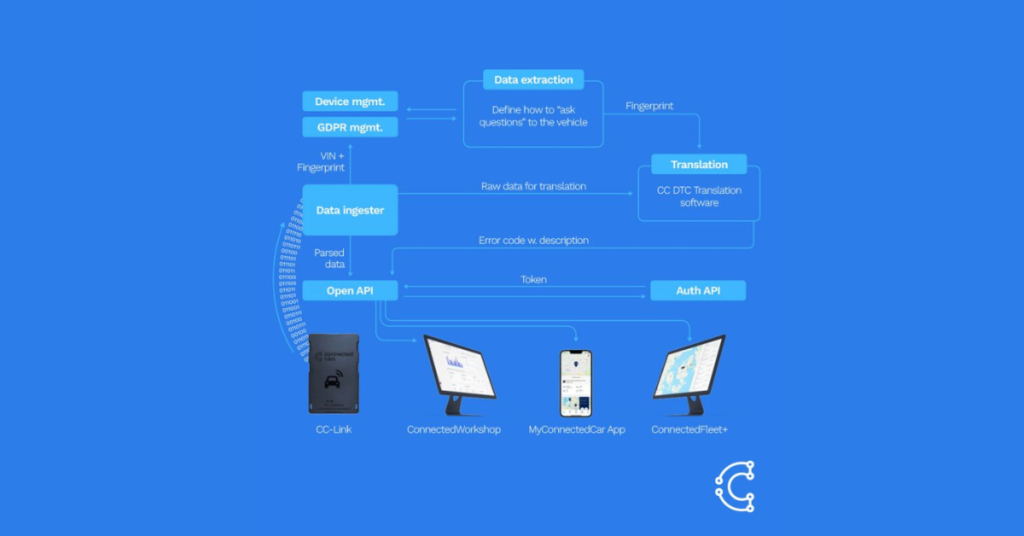
From the beginning, Connected Cars solutions were designed with the utmost data security legislation compliance in mind. It covers all aspects of data handling:
1. Gathering consent
To ensure full compliance with GDPR and marketing regulations, we acquire high-quality consent at each stage of the user journey. We require consent for all features to function, providing the user with complete control over how we process, store, and use their data.
2. Consent management
A list of consents is assigned to a unit based on the vehicle’s users.
The list of consents governs what data can be collected and for how long. For example, vehicle status consent allows for the collection of the most recent GPS location, whereas trip consent allows for the gathering of prior GPS positions as well.
We utilize consent to filter data on both the device and the server. Consent is employed to filter configurations before they are delivered to CC-Link.
Before storing data, ingestion servers examine consent. The established list of consents and their list of data points can be customized.
3. Data collection and visibility
We limit access to data based on the type of user and their connection to the vehicle. Users have access to data for an (unlimited) period of time.

Conclusion
Ultimately, cybersecurity and data privacy in connected vehicles are crucial to telematics. Telematics companies must protect the sensitive data collected and sent by vehicles as they use telematics technology more. This keeps drivers and passengers safe and private and helps people trust the technology more.






